Kids & Teens: Building Smart Habits Early
Children and teenagers who learn money skills early build stronger financial confidence, better decision-making, and long-term independence.
Why Start Money Lessons Early?
Research from the CFPB and University of Cambridge shows that children form lifelong financial habits by age 7. Teens begin making real financial decisions shortly after — first jobs, debit cards, online spending, and early credit exposure.
- Build confidence handling money independently
- Prevent costly mistakes like debt and overspending
- Strengthen family money conversations
- Support long-term habits around saving & planning
At V & V Advisors, we believe financial literacy is a core life skill — just like reading or math.
For Kids (Ages 6–12)
Kids learn best through repetition, visuals, and hands-on activities. At this age, financial education should be fun, simple, and rooted in everyday life.
| Concept | Activity | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Saving & Sharing | Use three jars labeled Save, Spend, Share. | Shows purpose-based saving and generosity. |
| Needs vs Wants | Sort items into “needs” and “wants” using pictures. | Builds decision-making skills. |
| Goal Setting | Have kids draw something they want to save for. | Encourages patience and planning. |
| Counting Money | Use coins/bills or digital money games. | Improves numeracy & real-world awareness. |
Source: FDIC Money Smart for Young People
For Teens (Ages 13–18)
Teens begin making real financial decisions — earning money, spending online, opening bank accounts, and preparing for education or career paths.
| Topic | What to Learn | Skill Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Budgeting | Learn the 50/30/20 rule using real income or allowance. | Teaches intentional planning. |
| Understanding Credit | Use credit-score simulators to see impacts of borrowing. | Builds responsible borrowing awareness. |
| Banking Skills | Practice deposits, transfers, and reading statements. | Supports real-world readiness. |
| Online Spending Safety | Learn about scams, subscriptions, and privacy. | Promotes secure digital habits. |
| Earning Money | Explore part-time work or small entrepreneurship. | Develops independence & work ethic. |
Source: CFPB Youth Financial Education

What Skills Should Kids & Teens Learn at Each Stage?
Based on guidance from the Jump$tart Coalition and CFPB, children and teens build financial capability in stages:
| Age Range | Financial Skills Developing |
|---|---|
| 5–7 | Recognizing money, simple choices, saving small amounts. |
| 8–12 | Setting goals, understanding trade-offs, earning small allowances. |
| 13–15 | Budgeting basics, early banking skills, online money safety. |
| 16–18 | Credit awareness, evaluating needs vs wants, planning for college or career. |
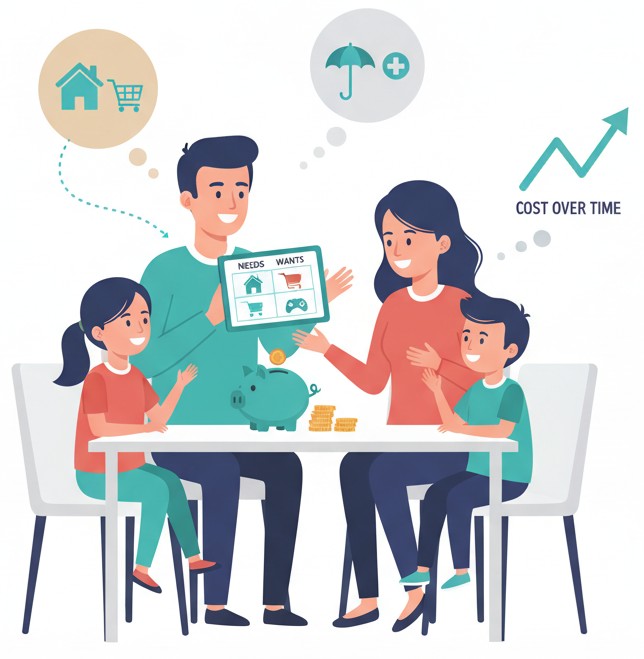
Family Money Conversations
Research shows kids learn the most about money from parents and caregivers — not from school. Here are simple conversations that help build confidence:
- “Here’s how our family plans for big purchases.”
- “This is how we compare needs and wants.”
- “We save for emergencies because unexpected things happen.”
- “Let’s look at how much this item costs over time.”
These conversations build healthy, open relationships with money.

50/30/20 Budget Breakdown
Teens can use the 50/30/20 method to structure real income from allowance or part-time work.
| Category | Description | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Needs | Essentials such as transportation, school supplies, small personal expenses. | 50% |
| Wants | Clothes, entertainment, hobbies, outings. | 30% |
| Savings | Emergency fund, future goals, or large purchases. | 20% |
Trusted Budget Calculators
| SoFi | Interactive 50/30/20 budgeting tool. | Visit → |
| NerdWallet | Budgeting tools and education for teens and adults. | Visit → |
| Bankrate | Easy budgeting and spending planners. | Visit → |