Understanding Risk & Family Protection
Every family faces risks — unexpected events that can impact health, income, or financial stability. When you understand these risks clearly, you can build a protection plan that keeps your family secure no matter what life brings.
What Do We Mean by “Risk”?
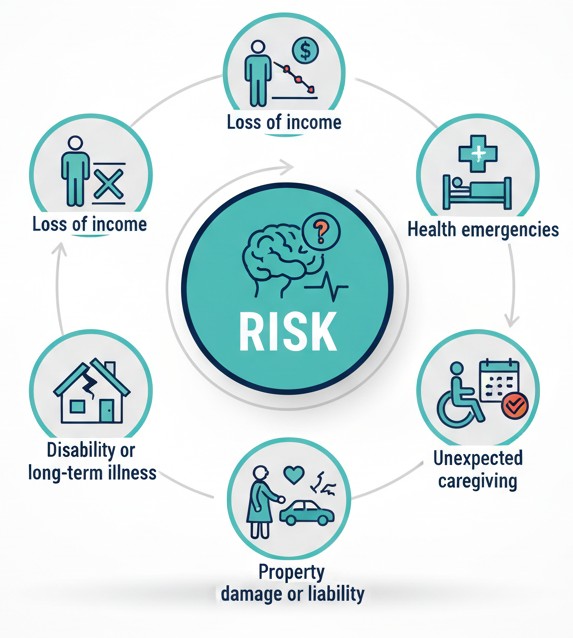
In personal finance, risk refers to the possibility that an unexpected event could create emotional or financial hardship. These events are often sudden, costly, and out of your control — which is why families benefit from preparing for them in advance.
- Loss of income
- Health emergencies
- Disability or long-term illness
- Property damage or liability
- Unexpected caregiving
The Four Major Types of Family Risk
Research from NAIC, CFPB, and the Federal Reserve shows that most households face four major categories of risk. Understanding these helps families build protection thoughtfully and intentionally.
| Risk Type | Examples | Impact on Family |
|---|---|---|
| Income Risk | Job loss, disability, death of an earner | Immediate financial hardship, long-term instability |
| Health Risk | Illness, injury, chronic conditions | High medical costs, time off work |
| Property & Liability Risk | Home damage, auto accidents, lawsuits | Unexpected large expenses or legal exposure |
| Legacy & Family Risk | Unplanned caregiving, lack of estate documents | Family stress, delayed wealth transfer |
The Household Vulnerability Model
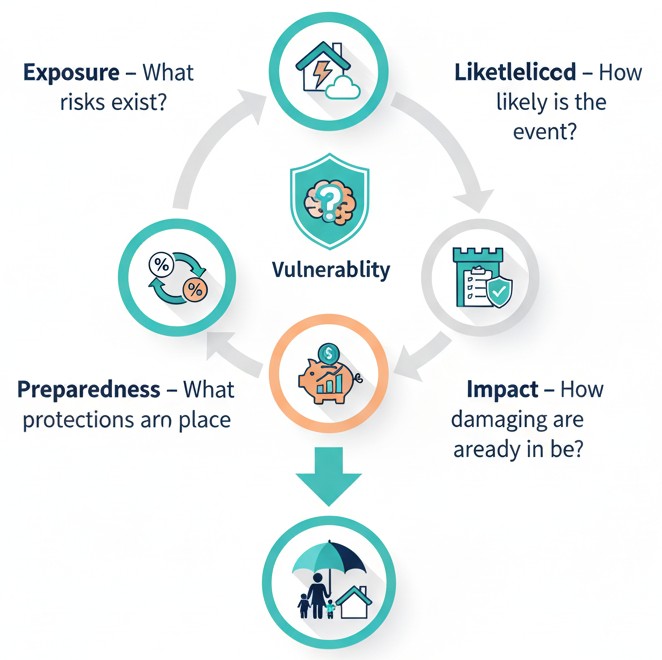
At V & V Advisors, we use a simple framework to help families identify where they may be financially vulnerable. This model aligns with research from the CFPB on how households recover from financial shocks.
- Exposure — What risks exist?
- Likelihood — How likely is the event?
- Impact — How damaging would it be?
- Preparedness — What protections are already in place?
When a risk has high impact and low preparedness, it becomes a priority for protection.
The 3-Layer Family Protection Framework
Families are strongest when they build protection in layers. At V & V Advisors, we teach a simple but powerful structure:
| Protection Layer | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Layer 1: Everyday Safeguards | Stabilize short-term shocks | Emergency fund, disability insurance, health insurance |
| Layer 2: Long-Term Security | Protect income & generational goals | Life insurance, income replacement, long-term care planning |
| Layer 3: Legacy & Transfer | Ensure smooth wealth transition | Power of Attorney, wills, trusts, beneficiary planning |
Real-World Family Scenario
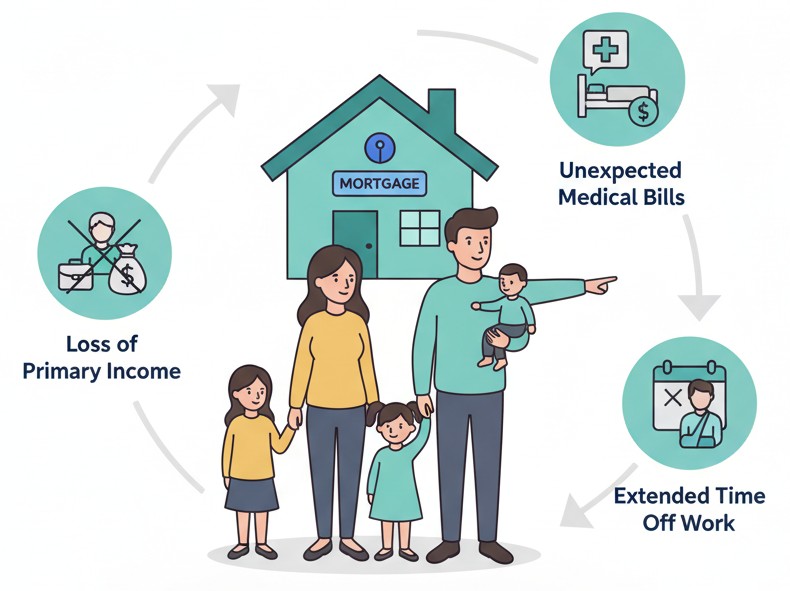
A family with two incomes, a mortgage, and young children faces a set of predictable risks. The most financially harmful ones are:
- Loss of a primary income
- Unexpected medical bills
- Extended time off work due to injury or caregiving
According to the Federal Reserve, 44% of Americans cannot cover a $1,000 emergency without borrowing, which makes thoughtful protection planning even more important.
Matching Risks With Protection Tools
| Risk | Protection Tools |
|---|---|
| Income loss | Life insurance, disability insurance, emergency fund |
| Health emergencies | Health insurance, supplemental benefits |
| Property damage or liability | Homeowners, renters, auto, umbrella insurance |
| Legacy & caregiving needs | Wills, trusts, POA, long-term care planning |
Family Protection Checklist
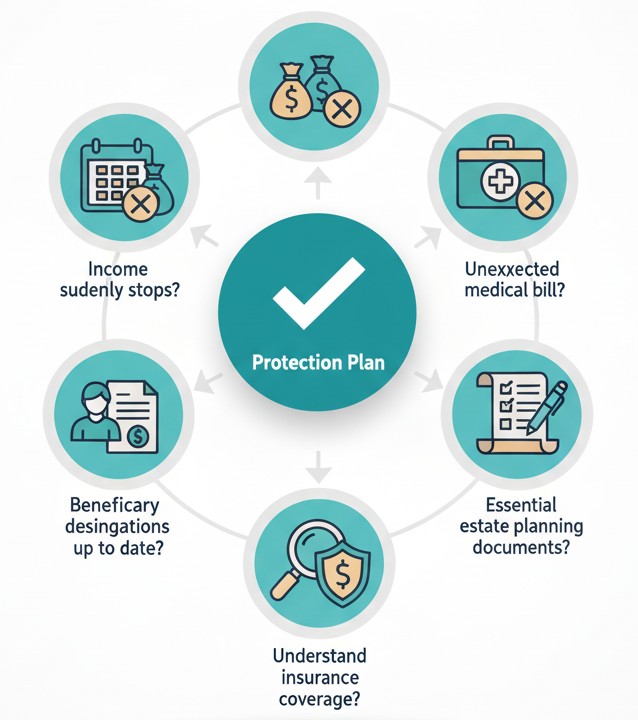
- Do you have a plan if income suddenly stops?
- How would your family handle an unexpected medical bill?
- Are beneficiary designations up to date?
- Do you have essential estate planning documents?
- Do you understand your current insurance coverage and gaps?